- 제목
- [2022] [배윤상] Submicron-thick, mixed-matrix membranes with metal-organic frameworks for CO2 separation: MIL-140C vs. UiO-67
- 작성일
- 2024.01.29
- 작성자
- 에어로겔소재연구센터 관리자
- 게시글 내용
-
Submicron-thick, mixed-matrix membranes with metal-organic frameworks for CO2 separation: MIL-140C vs. UiO-67
Abstract
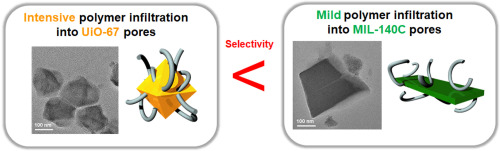
High-performance thin-film mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) were prepared using two types of zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), MIL-140C and UiO-67; both were dispersed in a polymer matrix for CO2 separation. A poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-poly(oxyethylene methacrylate) (PGO) copolymer was synthesized via one-pot free-radical polymerization and used as an adhesive matrix to allow intimate interfacial contact with the MOF fillers, resulting in 600 nm-thick defect-free MMMs with uniform dispersion. Both fillers comprise the same building blocks but have different pore sizes, structures, and particle morphologies. The pores of UiO-67 are 3D cage-like with a polyhedral morphology and were larger than the 1D channel-like pores of MIL-140C, having a rod-like morphology. The use of two fillers led to different degrees of polymer infiltration into the MOF pores, resulting in different CO2 separation performances. Overall, the MMMs with MIL-140C showed greater CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 selectivities than those with UiO-67 because of the well-defined micropores resulting from mild polymer infiltration and structural advantages such as a high aspect ratio. The best separation performance was achieved at 20% of MIL-140C loading (CO2 permeance of 1768 GPU and CO2/N2 selectivity of 38), lying in the commercial criteria required for post-combustion CO2 capture.