- 제목
- [2022] [변재철] Homogeneous One-Step Immunoassay Based on Switching Peptides for Detection of the Influenza Virus
- 작성일
- 2024.01.29
- 작성자
- 에어로겔소재연구센터 관리자
- 게시글 내용
-
Homogeneous One-Step Immunoassay Based on Switching Peptides for Detection of the Influenza Virus
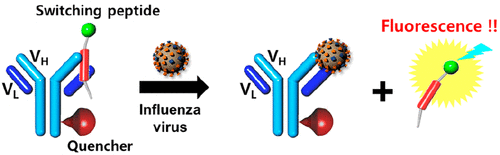
ABSTRACT:In this study, a homogeneous one-step immuno-assay based on switching peptides is presented for the detection ofinfluenza viruses A and B (Inf-A and Inf-B, respectively). The one-step immunoassay represents an immunoassay method that doesnot involve any washing steps, only treatment of the sample. In thismethod,fluorescence-labeled switching peptides quantitativelydissociate from the antigen-binding site of immunoglobulin G(IgG). In particular, the one-step immunoassay based on solubledetection antibodies with switching peptides is called a homogeneous one-step immunoassay. The immunoassay developed usesswitching peptides labeled with two types offluorescence dyes (FAM and TAMRA) and detection antibodies labeled with two typesoffluorescence quenchers (TQ2 for FAM and TQ3 for TAMRA). The optimal switching peptides for the detection of Inf-A and Inf-B have been selected as L1-peptide and H2-peptide. The interactions between the four kinds of switching peptides and IgG havebeen analyzed using computational docking simulation and SPR biosensor. The location of labeling for thefluorescence quenchershas been determined based on the distance between thefluorescence dyes of the switching peptides and thefluorescence quenchers,calculated on the basis of the efficiency offluorescence quenching, using the Förster equation. To demonstrate the feasibility of theone-step immunoassay, binding constants (KD) have been calculated for detection antibodies against Inf-A and Inf-B with targetantigens (Inf-A and Inf-B) and switching peptides (L1- and H2-peptides), using an isotherm model. The immunoassay has beendemonstrated to be feasible using antigens as well as real samples of Inf-A and Inf-B with a critical cycle number (Ct). Theimmunoassay has also been compared to other commercially available rapid test kits for Inf-A and Inf-B and found to be far moresensitive for detection of Inf-A and Inf-B over the entire detection range.